Tagged: leadership
Leadership: Mini-Motivators of Motivation
In my journey through leadership , I learn a lot through experiences and observations… here is one observation:
We all work for different things and we are all entitled to our personal (or not) reasons for what motivates us. Motivation is probably the single most powerful thing that keeps an employee (willingly) at a company.
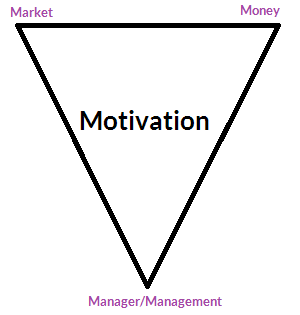
Motivation comprises of many things; I will not pretend to be the expert on motivation (or leadership) but for me and maybe for you (and possibly the general public), I think it breaks down into three mini-motivators.
- Market: Product/Space you work on/in, the day-to-day things you do
- Money: How much you get paid to do what you do
- Manager/Management: Your belief, trust and/or respect for the person or people who is/are your leader(s).
To ensure that people are motivated, all leaders should focus and be challenged to ensure that all three mini-motivators are attended to as in an ideal job, one would have a good mix of all three.
So the question is: What happens when you start taking things away? or what if you had to focus on just one to grow your team? In my opinion (and many others as well), “Manager/Management” is the silver bullet.
People work for great managers/management teams and will continue to work for them even if the pay is low or the job is boring; however, if you take away the great manager/management team and give the person a great market opportunity and/or over compensate, eventually, the individual(s) will leave for other opportunities where they feel they will also get the “manager/management” balance.
There have been quite a few times when I have heard the phrase “People don’t leave companies, they leave managers” and slowly, it has started to make sense.
Leaders must focus on motivation and be managers that are looked up to; if you have leaders who are not respected and looked up to, or “followed“; you have a motivation problem and (good) people will leave.
Horizontal Management – Maintaining momentum: Keep progress moving
While machines might give the same level of output everyday, the same doesn’t apply to people.
In a real environment, each member’s momentum and motivations will change without notice. This requires management to step in and make sure they are constantly evolving the processes so that members will remain motivated. Leadership is important to motivate key players, channel information to keep everyone engaged and make working horizontally routine. To accomplish this, management might bring in an outside champion, who will help wring in new ideas and “fresh” stream of motivation. Instead of looking at a project as a whole, it should be broken down into smaller goals that are realistic and achievable. Management should encourage and build on small success, to demonstrate that it was an important milestone and motivate members. Progress and results should be demonstrated so that members can all acknowledge the ongoing progress and success. Management can keep the members interests by ensuring that they are always focused on achieving the goals that were set, and if deviation is detected, corrective action is taken to bring things back on track.
A horizontal team is dynamic as it is always changing, management needs to account for its dynamic nature and make necessary adjustments to accommodate/adapt to the change. Money is probably the best motivator, but too much money too early in the process can hinder individual initiative and prevent people from innovating. Since horizontal structures focus on team collaboration, a downfall is that meetings can go on forever and schedules can be missed; this can unmotivated some members who feel that decisions are not being made in a timely manner, which is why management can implement deadlines which will help practitioners develop a common schedule and manage workloads effectively so that the projects momentum is kept at a steady pace.
[Source: Moving from the Heroic to the everyday: Hopkins, Couture, Moore]
Horizontal Management – Building support structures: To keep Horizontal team in check with Vertical roles
Even though a “horizontal structure” is flat in nature, it does still need a (vertical) support structure.
The main purpose of a support structure is to help managers build lasting relationships and achievements with teams. There are two basic type of support structures that managers can mix and match when building or working with teams, depending on the requirements as each has its own attributes.
- Informal structures don’t define rigid roles and responsibilities, they are open to interpretation and people can define their own roles and swap roles as needed, hence they are less resource intensive, more flexible and less binding on members; Informal structures help promote open discussion and communication among its team members; and
- Formal structures are more rigid and roles/titles might be defined where members have specific responsibilities; this makes them more resource intensive but less ambiguous; they require some logistical skill and expertise to implement. These structures are great when consistency and quality are important factors.
It’s important for management to recognize what type of structure needs to be in place and when its put in place; as “when” a structure is erected, it can play an important role in the success of the teamwork initiative. If too much formality is introduced early, people might feel there is no difference in the “horizontal structure” and the “vertical structure” where vertical structures are rigid, formal and bureaucratic and would be less motivated to work with the initiative. In contrast, waiting too long to build a support structure or the lack of a support structure can hinder the ability of the team to successfully work together as a team, especially when they need to be able to adapt when in tight spots.
Since the resources and effort required are greater when setting up formal structures, informal structures are great for short projects, however when the projects will go on for a long period of time or are of large scale, formal structures would be more suited as they are less ambiguous and will stay well formed longer (as they are more solid than informal structures).
Authority and roles in informal structures are more ambiguous and can be swapped around; In formal structures, the roles and responsibilities are more definitive, hence less ambiguous and in that regard, formal structures would work best in situations where important decisions need to be made.
[Source: Moving from the Heroic to the everyday: Hopkins, Couture, Moore]
Horizontal Management – Mobilizing team and networks: Ready for action
A team that does not work well not only is not a team; but is a blocker towards any success. It is a team (not) that does no work. – yes the not is from Borat.
We must be able to organize teams and networks to be ready for action as this helps the team get off the ground and moving. In order to help get things going as smooth as possible we can focus on a few key elements that can build teamwork and networks, these are leadership, teamwork attitude, common understanding and trust.
Leadership: In my experience, I have always enjoyed working on projects when I was able to be the leader, I think this is inherent to our nature that most of us want to be leaders instead of followers as it makes us feel important and think that we have make a significant contribution to the project. When working as a team, one of the great benefits (that most do not realize) is that the leadership can be shared equally among the team members, it can and should shift from person to person depending on what is required and the person’s strengths, this gives everyone a feeling of accomplishment and an equal and important say in the processes (even if it may not be). When working horizontally team members should be allowed to have debates, open discussions as they are key methods of identify opportunities and resolve conflicts that may arise….. so long as you can focus and move forward.
Teamwork: Rewarding team members to play nicely as a team always gets peoples motivations up. Teamwork makes a horizontal partnership cohesive so management should encourage early team building activities and open engagement that help develop a sense of collective ownership. This can be encouraged by giving incentives to work successfully as a team, such as recognizing members for their team efforts by giving awards and rewards.
Common Language: Recently I worked on a project where I was using the phrase “data entry” to describe an action where “any user enters data using a graphical user interface”. One of the team members was having a very hard time following the discussion because to him “data entry” was specific to “data entry personnel” (people hired to do data entry), who used a specific data entry user interface that was different than the user interfaces used by others, this was because they didn’t need the pretty features as all they did was repetitive data entry. This is why it becomes very important that the team members have a common mental model and have developed a vocabulary that is understood by all as this helps develop a working culture where misunderstandings or unclear terms will be kept to a minimum.
Trust: Trust is very important in maintaining relationships, it is the glue that holds a team together, if someone does not trust other members in a team, or does not fully place their trust in the team they will not be completely open and might not want to take part in discussions or coordinated efforts. The need for trust makes it important to invest in relationships and build credibility, this can be done by undertaking small tasks, being open and honest with others and delivering what was promised. When team members trust each other they will be willing to risk more together.
[Source: Moving from the Heroic to the everyday: Hopkins, Couture, Moore]
Leadership and Followship – your twitter followers don’t count.
In my opinion, Followship is the single measure that can tell you how great of a leader you are.
A leader has the ability to motivate, collaborate with, and influence others to commit to and do what is on his/her agenda. For this to happen, you need people who will commit to following this leader.
A leader would have followers who are not just his/her direct reports; followers would be from other teams who will do whatever they can to assist this leader be successful.
How do you measure followship? Is someone doing something for you because they fear they must? Or because they want to?
True followers will be engaging and will continue to challenge the leader by providing constructive feedback. Followers who follow because they have to will not be engaging and will simply do what you ask them unwillingly with negative comments and attitude.
A leader must have followers; without followers you have no one to lead.